| instance | ||
| migrations | ||
| modui | ||
| nsfw_model | ||
| templates | ||
| tests | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| .mailmap | ||
| 0x0-prune.service | ||
| 0x0-prune.timer | ||
| 0x0-vscan.service | ||
| 0x0-vscan.timer | ||
| cleanup.py | ||
| fhost.py | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| mod.css | ||
| mod.py | ||
| modui.webp | ||
| nsfw_detect.py | ||
| pyproject.toml | ||
| README.rst | ||
| requirements.txt | ||
The Null Pointer
This is a no-bullshit file hosting and URL shortening service that also runs 0x0.st. Use with uWSGI.
Configuration
To configure 0x0, copy instance/config.example.py to
instance/config.py, then edit it. Resonable defaults are
set, but there's a couple options you'll need to change before running
0x0 for the first time.
By default, the configuration is stored in the Flask instance directory. Normally, this is in ./instance, but it might be different for your system. For details, see the Flask documentation.
To customize the home and error pages, simply create a
templates directory in your instance directory and copy any
templates you want to modify there.
If you are running nginx, you should use the
X-Accel-Redirect header. To make it work, include this in
your nginx config’s server block:
location /up {
internal;
}where /up is whatever you’ve configured as
FHOST_STORAGE_PATH.
For all other servers, set FHOST_USE_X_ACCEL_REDIRECT to
False and USE_X_SENDFILE to True,
assuming your server supports this. Otherwise, Flask will serve the file
with chunked encoding, which has several downsides, one of them being
that range requests will not work. This is a problem for example when
streaming media files: It won’t be possible to seek, and some ISOBMFF
(MP4) files will not play at all.
To make files expire, simply run
FLASK_APP=fhost flask prune every now and then. You can use
the provided systemd unit files for this:
0x0-prune.service
0x0-prune.timerMake sure to edit them to match your system configuration. In
particular, set the user and paths in
0x0-prune.service.
Before running the service for the first time and every time you
update it from this git repository, run
FLASK_APP=fhost flask db upgrade.
Moderation UI
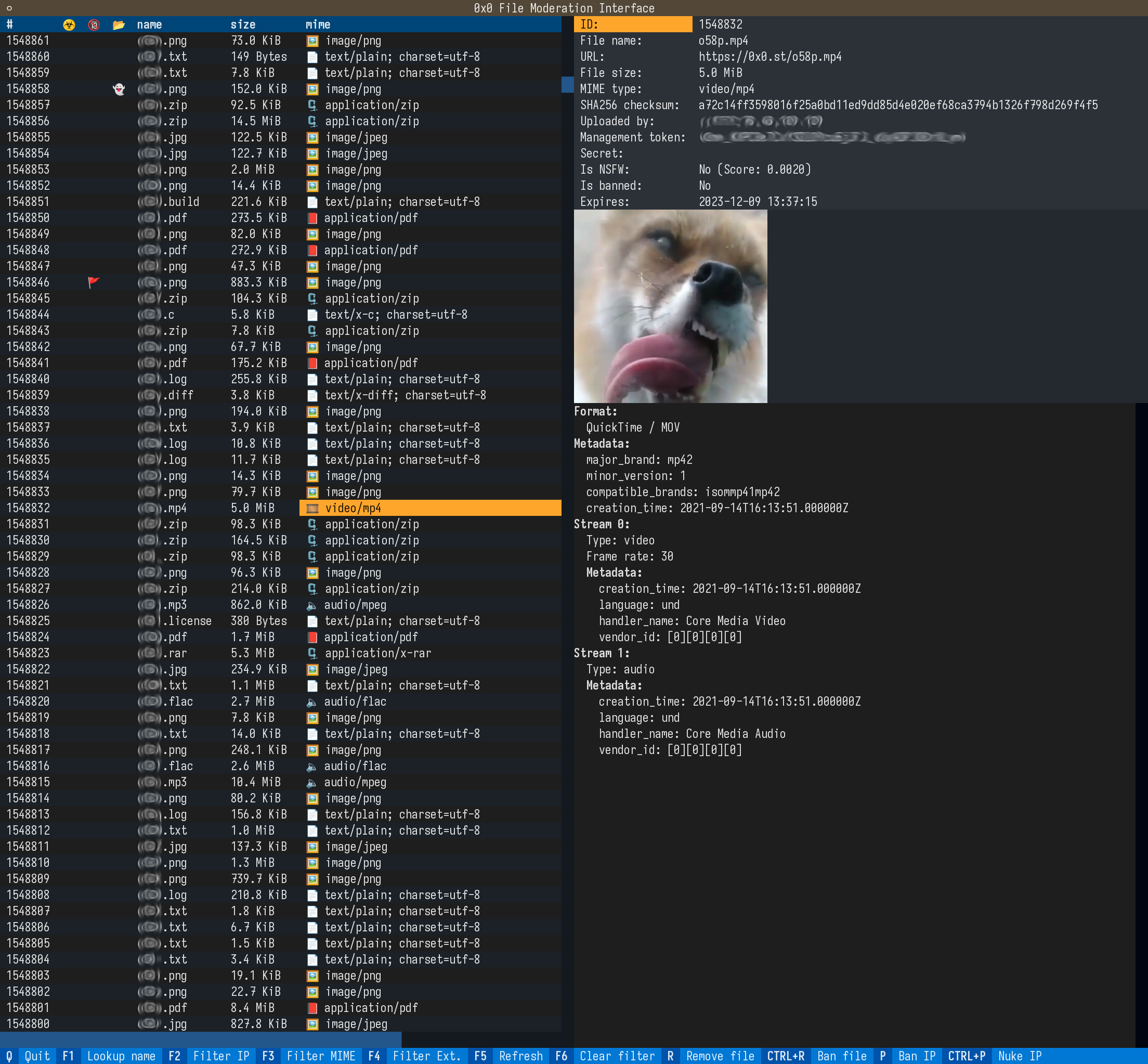
0x0 features a TUI program for file moderation. With it, you can view a list of uploaded files, as well as extended information on them. It allows you to take actions like removing files temporarily or permanently, as well as blocking IP addresses and associated files.
If a sufficiently recent version of python-mpv with libmpv is present
and your terminal supports it, you also get graphical file previews,
including video playback. Upstream mpv currently supports sixel
graphics, but there is an open pull
request that adds support for the kitty graphics
protocol. For this to work, set the MOD_PREVIEW_PROTO
option in instance/config.py.
Requirements:
Optional:
- python-mpv (graphical previews)
- PyAV (information on multimedia files)
- PyMuPDF (previews and file information for PDF, XPS, EPUB, MOBI and FB2)
- libarchive-c (archive content listing)
Note
Mosh currently does not support sixels or kitty graphics.
Hint
You may need to set the COLORTERM environment variable
to truecolor.
Tip
Using compression with SSH (-C option) can significantly
reduce the bandwidth requirements for graphics.
NSFW Detection
0x0 supports classification of NSFW content via Yahoo’s open_nsfw Caffe neural network model. This works for images and video files and requires the following:
- Caffe Python module (built for Python 3)
- PyAV
Virus Scanning
0x0 can scan its files with ClamAV’s daemon. As this can take a long
time for larger files, this does not happen immediately but instead
every time you run the vscan command. It is recommended to
configure a systemd timer or cronjob to do this periodically. Examples
are included:
0x0-vscan.service
0x0-vscan.timerRemember to adjust your size limits in clamd.conf, including
StreamMaxLength!
This feature requires the clamd module.
Network Security Considerations
Keep in mind that 0x0 can fetch files from URLs. This includes your local network! You should take precautions so that this feature cannot be abused. 0x0 does not (yet) have a way to filter remote URLs, but on Linux, you can use firewall rules and/or namespaces. This is less error-prone anyway.
For instance, if you are using the excellent FireHOL, it’s very easy to create a group on your system and use it as a condition in your firewall rules. You would then run the application server under that group.